2016 한국음운론학회-서울대학교 언어연구소 및 언어학과 서울국제음운론학술대회 (12/16-17)
2016.12.07 17:37
2016 한국음운론학회-서울대학교 언어연구소 및 언어학과 서울국제음운론학술대회
일시: 2016년 12월 16-17일 금-토요일 09:30-18:00
장소: 서울대학교 인문대학 14동 B101호 (점심 식사 장소: 자하연(3층) 교수식당)
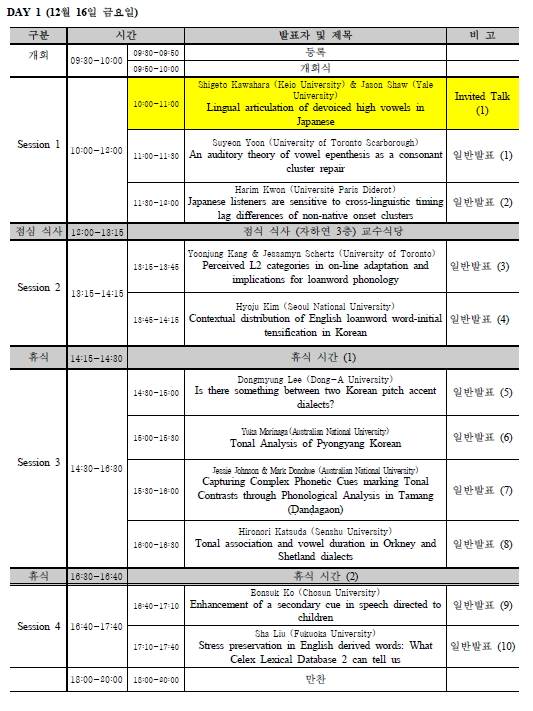
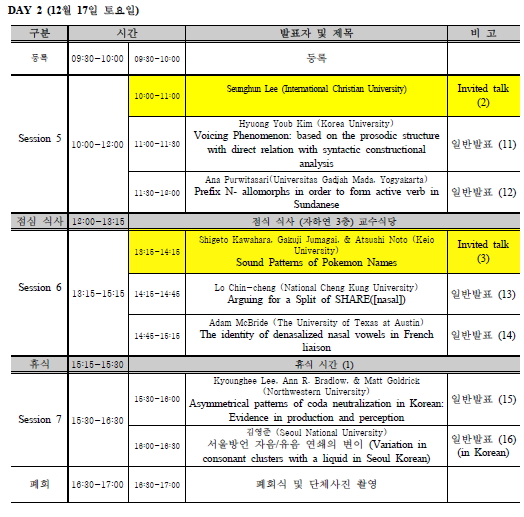
아래에는 세 초청강연의 초록을 첨부합니다. 참고하시기 바랍니다.
Lingual articulation of devoiced high vowels in Japanese
Shigeto Kawahara & Jason Shaw
Keio University & Yale University
High vowels in (Tokyo) Japanese are devoiced between two voiceless consonants. One question that has been debated in the literature is whether these vowels are simply devoiced or entirely deleted (e.g. Jun & Beckman 1993 vs. Kondo 2000). A related question is, if devoiced high vowels are deleted, then what is the consequence for moraification and syllabification (Hirayama 2009)? We shed new light on these debates using ElectroMagnetic Articulography (EMA) by examining lingual gestures of devoiced high vowels. Our results suggest that high vowels are optionally deleted, but that both moras and syllables that host these high vowels remain intact.
We recorded lingual trajectories of several dyads that differ in the devoicability of high vowels; e.g. [ɸusoku] “shortage” and [ɸuzoku] “attachment”. We generally found that the tongue dorsum does not rise as much for devoiced vowels as for voiced counterparts. We next tested the possibility that the vocalic gesture is in fact targetless for devoiced high vowels (cf. “phonetic underspecification”: Keating 1988). This hypothesis was assessed in three steps. First, articulatory trajectories were decomposed into a set of cosine components through Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). Second, based on the obtained DCT coefficients, we generated noisy null trajectories of the linear interpolation between the preceding and the following vowel, which allowed us to simulate how the linear interpolation would be realized given the natural variability that exists in our data (Shaw & Gafos 2015). Third, we trained a naïve Bayesian classifier to calculate the posterior probabilities of “full target” vs. “no target”, token-bytoken. This three-step analysis shows that lingual gestures are optionally deleted.
We then turn to the question of what happens to moras and syllables of these deleted vowels. Phonological evidence suggests that both moras and syllables remain (Tsuchida 1997; Kawahara 2015), implying the heterosyllabic parsing of the resulting cluster (e.g. [ɸ.so.ku] instead of [ɸso.ku]). We argue that the articulation data are compatible with this phonological evidence. First, the deletability hierarchy that we found in our experiment follows the syllable contact law (Venneman 1988), supporting the heterosyllabic parsing of the resulting consonant cluster. Second, the temporal stability analysis (Browman & Goldstein 1988) is also compatible with the heterosyllabic parsing in that the right edge of the second consonant of the cluster is most tightly coordinated with the following vowel.
Time permitting, we will touch upon our follow-up experiments to confirm the existence of “fricative syllables” as well as the activity of syllable contact law in Japanese.
Shigeto Kawahara & Jason Shaw
Keio University & Yale University
High vowels in (Tokyo) Japanese are devoiced between two voiceless consonants. One question that has been debated in the literature is whether these vowels are simply devoiced or entirely deleted (e.g. Jun & Beckman 1993 vs. Kondo 2000). A related question is, if devoiced high vowels are deleted, then what is the consequence for moraification and syllabification (Hirayama 2009)? We shed new light on these debates using ElectroMagnetic Articulography (EMA) by examining lingual gestures of devoiced high vowels. Our results suggest that high vowels are optionally deleted, but that both moras and syllables that host these high vowels remain intact.
We recorded lingual trajectories of several dyads that differ in the devoicability of high vowels; e.g. [ɸusoku] “shortage” and [ɸuzoku] “attachment”. We generally found that the tongue dorsum does not rise as much for devoiced vowels as for voiced counterparts. We next tested the possibility that the vocalic gesture is in fact targetless for devoiced high vowels (cf. “phonetic underspecification”: Keating 1988). This hypothesis was assessed in three steps. First, articulatory trajectories were decomposed into a set of cosine components through Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). Second, based on the obtained DCT coefficients, we generated noisy null trajectories of the linear interpolation between the preceding and the following vowel, which allowed us to simulate how the linear interpolation would be realized given the natural variability that exists in our data (Shaw & Gafos 2015). Third, we trained a naïve Bayesian classifier to calculate the posterior probabilities of “full target” vs. “no target”, token-bytoken. This three-step analysis shows that lingual gestures are optionally deleted.
We then turn to the question of what happens to moras and syllables of these deleted vowels. Phonological evidence suggests that both moras and syllables remain (Tsuchida 1997; Kawahara 2015), implying the heterosyllabic parsing of the resulting cluster (e.g. [ɸ.so.ku] instead of [ɸso.ku]). We argue that the articulation data are compatible with this phonological evidence. First, the deletability hierarchy that we found in our experiment follows the syllable contact law (Venneman 1988), supporting the heterosyllabic parsing of the resulting consonant cluster. Second, the temporal stability analysis (Browman & Goldstein 1988) is also compatible with the heterosyllabic parsing in that the right edge of the second consonant of the cluster is most tightly coordinated with the following vowel.
Time permitting, we will touch upon our follow-up experiments to confirm the existence of “fricative syllables” as well as the activity of syllable contact law in Japanese.
High tone spread, prosodic binarity and MatchLexPhrase in Xitsonga
Seunghun J. Lee & Elisabeth Selkirk
International Christian University & University of Massachusetts at Amherst
This paper focuses on the theory of prosodic structure formation, providing support for the central Match theory idea that prosodic constituency essentially matches up with syntactic constituency at the word, phrase, and clause levels, except if some high ranked phonological markedness constraint(s) call for departures from the syntax (Selkirk 2011). One purpose of this paper is to elaborate the argument for a crucial combined role in the grammar of phonological phrasing in the Bantu language Xitsonga for a prosodic binarity
constraint on phonological phrase (ϕ) and a Match constraint requiring correspondence between syntactic phrases and phonological phrases. A second purpose of this paper is to argue for a theory of prosodic structure formation in which tight restrictions are placed on the structural information appealed to in the constraints themselves, both the prosodic markedness constraints and the Match constraints on relation between syntactic and prosodic constituency.
The general, minimalist, hypothesis behind this enterprise is that complexities in prosodic structure formation arise through the interaction of very simple constraints from the syntacticprosodic constituency correspondence submodule and very simple constraints from the phonological markedness submodule.
Seunghun J. Lee & Elisabeth Selkirk
International Christian University & University of Massachusetts at Amherst
This paper focuses on the theory of prosodic structure formation, providing support for the central Match theory idea that prosodic constituency essentially matches up with syntactic constituency at the word, phrase, and clause levels, except if some high ranked phonological markedness constraint(s) call for departures from the syntax (Selkirk 2011). One purpose of this paper is to elaborate the argument for a crucial combined role in the grammar of phonological phrasing in the Bantu language Xitsonga for a prosodic binarity
constraint on phonological phrase (ϕ) and a Match constraint requiring correspondence between syntactic phrases and phonological phrases. A second purpose of this paper is to argue for a theory of prosodic structure formation in which tight restrictions are placed on the structural information appealed to in the constraints themselves, both the prosodic markedness constraints and the Match constraints on relation between syntactic and prosodic constituency.
The general, minimalist, hypothesis behind this enterprise is that complexities in prosodic structure formation arise through the interaction of very simple constraints from the syntacticprosodic constituency correspondence submodule and very simple constraints from the phonological markedness submodule.
Sound Patterns of Pokemon Names
Shigeto Kawahara1, Gakuji Kumagai2 and Atsushi Noto3
(1Keio University, 2,3Tokyo Metropolitan University)
This paper presents a case study of sound symbolism, cases in which certain sounds tend to be associated with particular meanings. The current study uses the corpus of all pokemon names available as of October 2016. This paper explores the effects of voiced obstruents and mora counts in Japanese pokemon names, and reveals that both of them impact pokemon characters’ size, weight, strength parameters, and evolution levels. In particular, the number of voiced obstruents in pokemon names positively correlates with size, weight, evolution levels, and general strength parameters, except for speed. We argue that this result is compatible with the Frequency Code Hypothesis proposed by Ohala. The number of moras in pokemon names positively correlates with size, weight, evolution levels and all strength parameters. Multiple regression analyses show that the effects of voiced obstruents and those of mora counts hold independently of one another. Not only does this paper offer a new case study of sound symbolism, it provides evidence that sound symbolism is at work when naming proper nouns. In general, the materials provided in this paper should be useful for undergraduate education in linguistics and psychology to attract students’ interests, as pokemon is very popular among current students.
Shigeto Kawahara1, Gakuji Kumagai2 and Atsushi Noto3
(1Keio University, 2,3Tokyo Metropolitan University)
This paper presents a case study of sound symbolism, cases in which certain sounds tend to be associated with particular meanings. The current study uses the corpus of all pokemon names available as of October 2016. This paper explores the effects of voiced obstruents and mora counts in Japanese pokemon names, and reveals that both of them impact pokemon characters’ size, weight, strength parameters, and evolution levels. In particular, the number of voiced obstruents in pokemon names positively correlates with size, weight, evolution levels, and general strength parameters, except for speed. We argue that this result is compatible with the Frequency Code Hypothesis proposed by Ohala. The number of moras in pokemon names positively correlates with size, weight, evolution levels and all strength parameters. Multiple regression analyses show that the effects of voiced obstruents and those of mora counts hold independently of one another. Not only does this paper offer a new case study of sound symbolism, it provides evidence that sound symbolism is at work when naming proper nouns. In general, the materials provided in this paper should be useful for undergraduate education in linguistics and psychology to attract students’ interests, as pokemon is very popular among current students.
댓글 0

2sisstore




